- March 10, 2023
- Posted by: Anna Rosenkranz
- Category: Blog

VLAN Types: What Are They and How They Work?
We’ll explain what VLAN is and cover common types of VLANs that exist today in the guide below.
Every TCP/IP computer network professional must be well-versed in the fundamental concept; of VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network). Understanding the different VLAN types and their benefits to business is crucial. In essence, VLAN is grouping one or more Local area networks to communicate with each other. It allows computers and users in the network to share in the broadcast domain. Its main purpose is to improve performance and security, and its membership can be configured via software with a simple network design.
This article delves deeper into VLAN types based on purpose, how they work and how they can be used. Read on to have a deeper understanding of how VLANs are implemented and configured.
What is VLAN and How Does It Work?
 A Computer Science Academic paper defines VLAN as LAN grouping for communication purposes. A LAN (Local Area Network is a single broadcast domain. A VLAN allows a group of devices available in one network to merge and form one logical network.
A Computer Science Academic paper defines VLAN as LAN grouping for communication purposes. A LAN (Local Area Network is a single broadcast domain. A VLAN allows a group of devices available in one network to merge and form one logical network.
A VLAN’s main characteristics are:
- It can span multiple switches.
- A VLAN increases the broadcast domains possible in a LAN.
- It makes terminal reallocations easier.
- Since an individual VLAN works as a LAN, it can reduce congestion by sharing traffic.
- All you need to change hosts or users of a VLAN is to get a new port-level configuration.
- It allows the use of a workstation with full bandwidth at each port.
- It reduces security risks as the number of hosts connected to the broadcast domain reduces.
- It reduces network traffic and latency.
- It is easy to manage even if it is located in different geographical locations.
Some of the benefits that come with using a VLAN include:
Better security: Using a VLAN reduces internal and external threats because users only access the network for their unique responsibilities, and attackers encounter boundaries when accessing the system.
Better quality of services: With VLAN, the traffic is high; thus, the user gets better performance. Plus, prioritizing in traffic is much easier.
Simplified management: VLAN simplifies administration for a network manager. The virtualization simplifies management, and you can use logic to group the users in the network. Also, you can easily control user access when a user moves to another workstation or group.
Easier error management: VLAN can easily troubleshoot an error because the network’s users are in different groups and isolated from one another.
In networking, VLANs are identified by a number. You must assign a port on a VLAN switch with a proper VLAN number ranging from 1-4094. The VLAN switch allows data exchange between various ports with the same VLAN number. All networks are larger than a single switch. Therefore, there are ways of sending traffic between two switches. A prime example is assigning a port on each network switch with a VLAN and running a cable between them.
How Is VLAN Used?
The main function of a VLAN is to separate layer 2 traffic. For instance, when one host cannot communicate with another host, a router is placed between them so they can exchange data. Another primary function of VLANs is securing data transfer between two hosts. Only members of a VLAN can access the network and data within it.
Types of VLANs Based on Purpose
There are five primary types of VLAN based on purpose, and they include;
Management VLAN
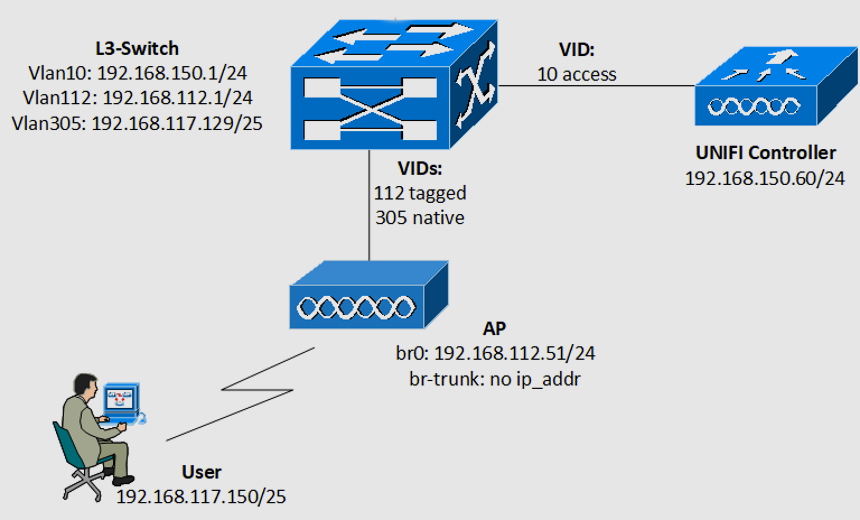 This is a type of VLAN set up for management traffic like an application logging or monitoring. It is configured to access the management capabilities of a switch. It is used to establish an IP connection to the switch from a workstation connected to a port in the VLAN. Any VLAN switch can be configured as the management VLAN if none is defined to serve as the management VLAN. In most cases, a network administrator proactively defines VLAN 1 as the management VLAN, enabling a loophole for an unauthorized connection to a switch. The management VLAN ensures that the management’s bandwidth is enough even when user traffic is high.
This is a type of VLAN set up for management traffic like an application logging or monitoring. It is configured to access the management capabilities of a switch. It is used to establish an IP connection to the switch from a workstation connected to a port in the VLAN. Any VLAN switch can be configured as the management VLAN if none is defined to serve as the management VLAN. In most cases, a network administrator proactively defines VLAN 1 as the management VLAN, enabling a loophole for an unauthorized connection to a switch. The management VLAN ensures that the management’s bandwidth is enough even when user traffic is high.
Data VLAN
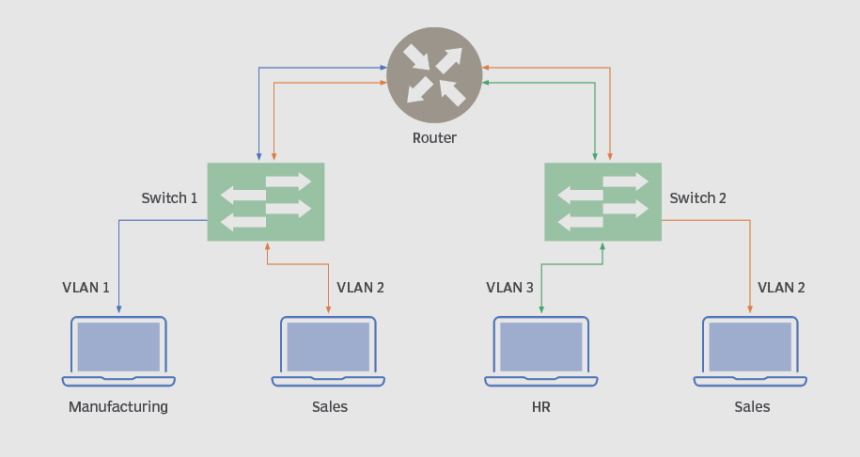 This is also called User VLAN because it is configured to carry only user-generated traffic. A VLAN can carry any traffic used to manage the switch or voice-based traffic, but it could never be a part of a data VLAN. The network can be designed depending on a group of users or workgroups. A good example is an institution. Its network workgroup could be developed based on departments. Essentially, data VLAN is where the end-user devices are assigned. You can have many data VLANs numbered or named to represent different groups of devices or departments like Finance VLAN, Sales VLAN, or Research VLAN.
This is also called User VLAN because it is configured to carry only user-generated traffic. A VLAN can carry any traffic used to manage the switch or voice-based traffic, but it could never be a part of a data VLAN. The network can be designed depending on a group of users or workgroups. A good example is an institution. Its network workgroup could be developed based on departments. Essentially, data VLAN is where the end-user devices are assigned. You can have many data VLANs numbered or named to represent different groups of devices or departments like Finance VLAN, Sales VLAN, or Research VLAN.
Voice VLAN
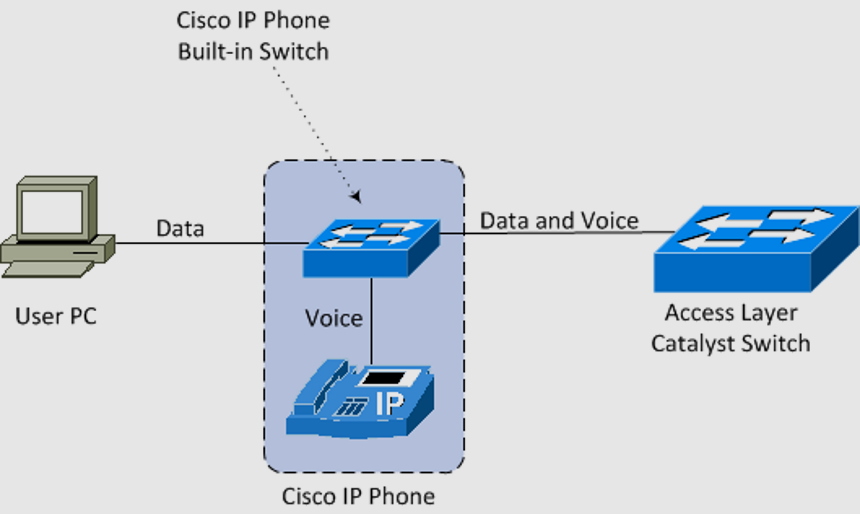 A voice VLAN is designed to carry voice traffic and is usually given high transmission priority over other network traffic types. Communication over the voice VLAN is not complete without phone calls. Phone calls are the dominating form of message transmission over the network. Emails and text messages are also used to inter-relate over the network, but real voice offers legitimacy and assurance. In many office environments, you will often find a computer and an IP phone on each desk. Connecting the computer and IP phone to a switch requires two cables to run from each device to the switch. Network administrators often aim to configure a network that supports Voice over IP (VoIP) with an assured bandwidth that provides great voice quality and can be routed around high-traffic areas on the network with zero delays.
A voice VLAN is designed to carry voice traffic and is usually given high transmission priority over other network traffic types. Communication over the voice VLAN is not complete without phone calls. Phone calls are the dominating form of message transmission over the network. Emails and text messages are also used to inter-relate over the network, but real voice offers legitimacy and assurance. In many office environments, you will often find a computer and an IP phone on each desk. Connecting the computer and IP phone to a switch requires two cables to run from each device to the switch. Network administrators often aim to configure a network that supports Voice over IP (VoIP) with an assured bandwidth that provides great voice quality and can be routed around high-traffic areas on the network with zero delays.
Default VLAN
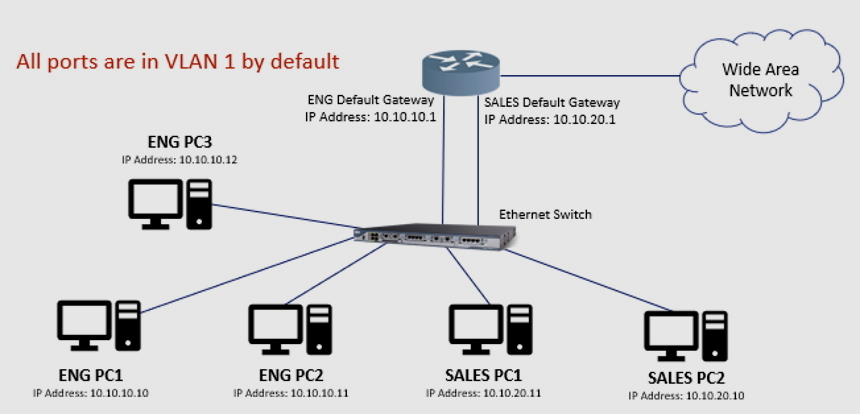 When the switch is booted up, all switch ports become members of the default VLAN. All the switch ports that participate in a default VLAN become a part of the same broadcast domain, thus allowing any device connected to any switch port to communicate with other devices connected to other switch ports. This is because all interfaces that are assigned in the default VLAN don’t tag the Ethernet frame as they leave. VLAN 1 is the default VLAN for Cisco switches.
When the switch is booted up, all switch ports become members of the default VLAN. All the switch ports that participate in a default VLAN become a part of the same broadcast domain, thus allowing any device connected to any switch port to communicate with other devices connected to other switch ports. This is because all interfaces that are assigned in the default VLAN don’t tag the Ethernet frame as they leave. VLAN 1 is the default VLAN for Cisco switches.
VLAN 1 has the same characteristics of any VLAN but you cannot delete or rename it. Another interesting fact is that Layer 2 control traffic like spanning tree protocol traffic and CDP are all associated with VLAN 1 and you cannot change it. Sometimes network administrators refer to the VLAN that has been assigned for interfaces and are not in use as default VLAN. This can be confusing as the VLAN is not really a default VLAN but a VLAN assigned to empty interfaces for security purposes.
Native VLAN
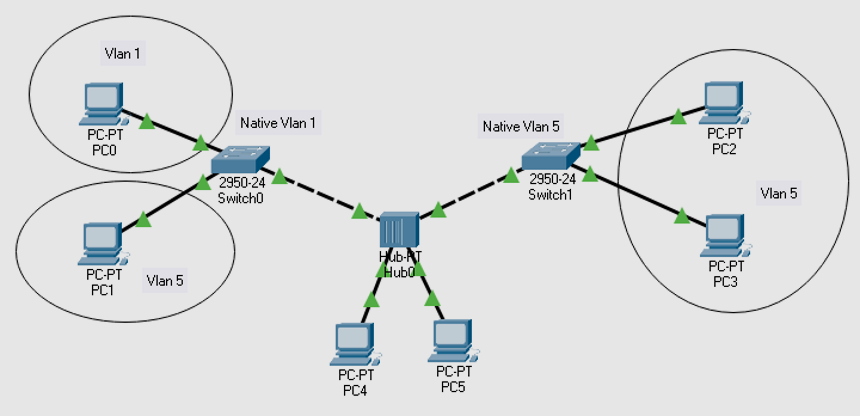 A native VLAN is the VLAN that identifies traffic that comes from each end of a trunk link and is only allocated to an 802.1Q trunk port. According EDUCBA, a trunk port is a switch port that carries traffic more than once in one VLAN. The trunk port receives untagged traffic on the native VLAN. Untagged traffic is traffic that does not come from any VLAN.
A native VLAN is the VLAN that identifies traffic that comes from each end of a trunk link and is only allocated to an 802.1Q trunk port. According EDUCBA, a trunk port is a switch port that carries traffic more than once in one VLAN. The trunk port receives untagged traffic on the native VLAN. Untagged traffic is traffic that does not come from any VLAN.
Other Important Types of VLANs
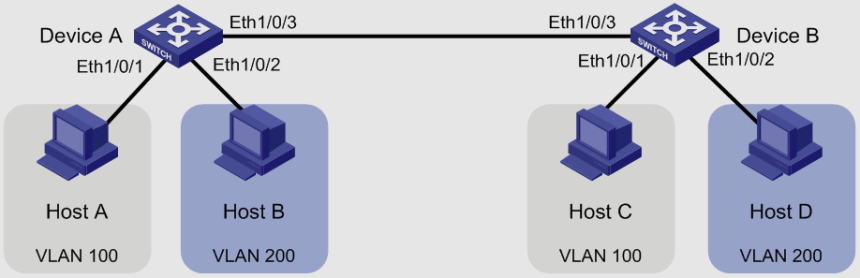 Besides the five primary types of VLANs based on purpose there are other crucial types of VLANs including;
Besides the five primary types of VLANs based on purpose there are other crucial types of VLANs including;
Port-based VLAN
These group virtual local area networks by port. With a virtual LAN you can configure a switch port manually to a member of VLAN. Since all other ports are configured with the same VLAN number, devices that are connected to the port will belong to the same broadcast domain. The main challenge with port-based VLAN is identifying the appropriate ports for each VLAN. You cannot know the VLAN membership just by looking at a switch’s physical port. You can only determine it by looking at the configuration information.
Protocol-based VLAN
This VLAN processes protocol-based traffic. You can use it to define filtering criteria for untagged packets. The smart switch often assigns untagged packets to VLAN 1 if you don’t configure a protocol-based VLAN. A protocol-based VLAN works in a multi-protocol environment, but is not practical in a predominantly IP based network. The only way to define a protocol based VLAN is by creating a group. The group must have a specific name and a one-to-one relationship with a VLAN ID and can have one to three protocol definitions and multiple ports. The smart switch will assign the group ID automatically.
Mac-based VLAN
A Mac-based VLAN allows the assigning of incoming untagged packets to a VLAN. Therefore, it classifies traffic according to the source Mac address on the untagged packet. A system-wide table that has Mac address to VLAN ID mappings exists for sharing Mac to VLAN configurations. The source Mac address of a priority or untagged packet is looked up the moment it arrives at the switch and there are entries in the Mac to VLAN table. A VLAN ID that corresponds to the found entry is assigned to the packet. The VLAN ID is verified against the VLAN table and if it is valid, ingress processing of the packet goes on. If it is not valid, the packet is dropped.
Final Thoughts
A VLAN is a custom network created from one or more LANs ad is identified by a number. The main difference between it and a LAN is that in LAN the network packet is sent to each device while in VLAN, the network packet is only sent to a specific broadcast domain. The main benefit of a VLAN is that it reduces the size of broadcast domains. It is important to understand different VLAN types before setting up a VLAN network for your business.
We have looked at the characteristics of a VLAN, its benefits and the reasons to implement it. The main purpose of implementing a VLAN is to improve performance and enhance security. You can easily configure a VLAN membership with a software that has a simple network design.
References
https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cis788-97/ftp/virtual_lans/index.html#WhatVLAN

